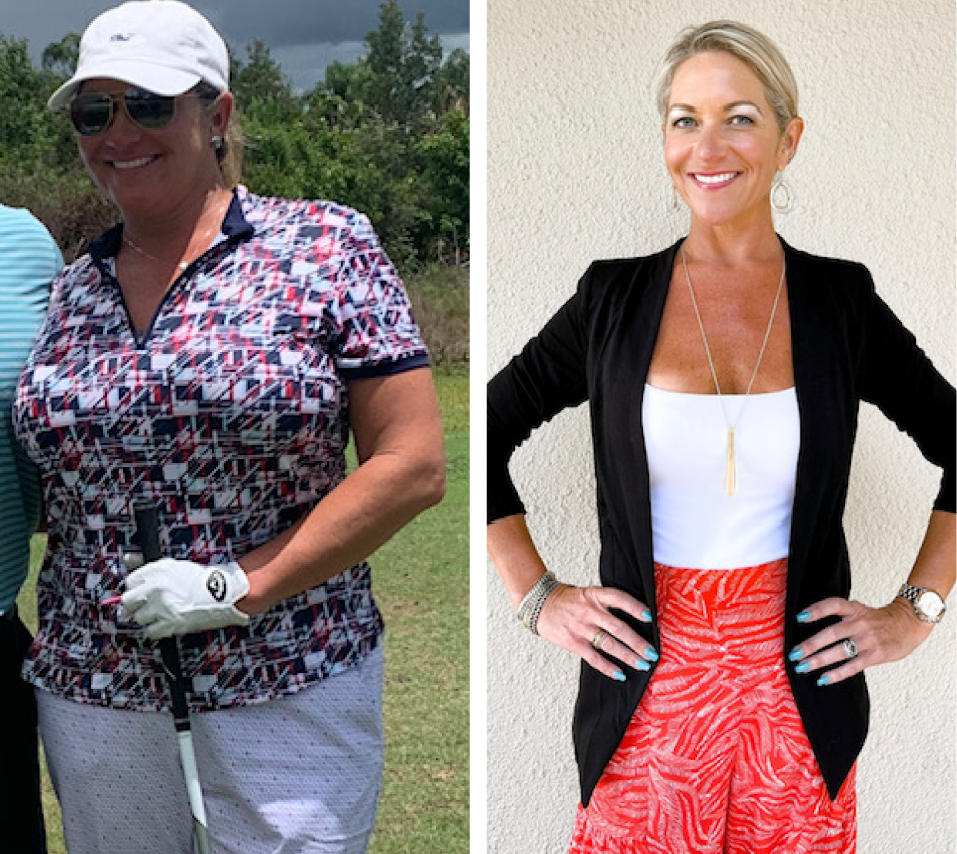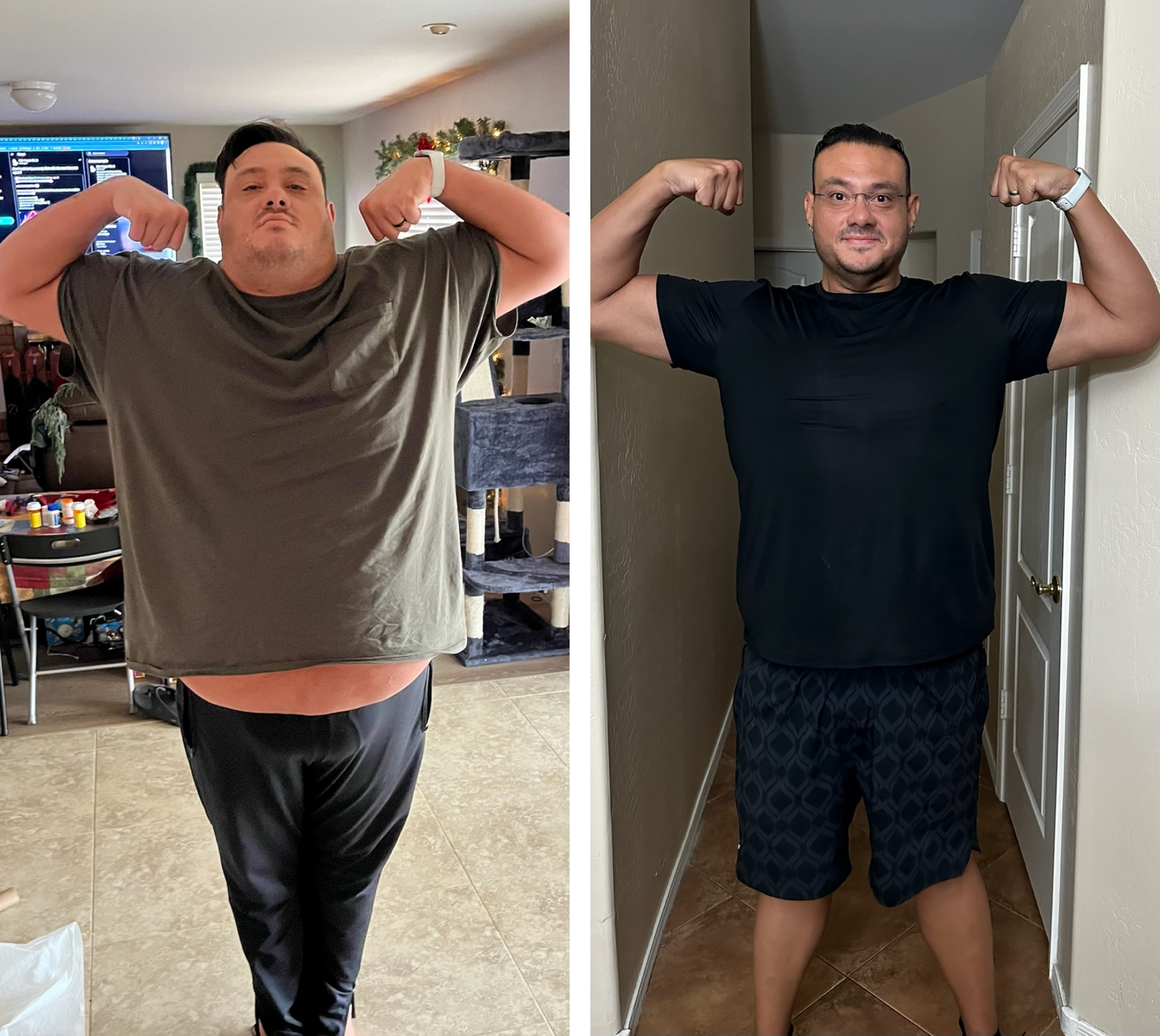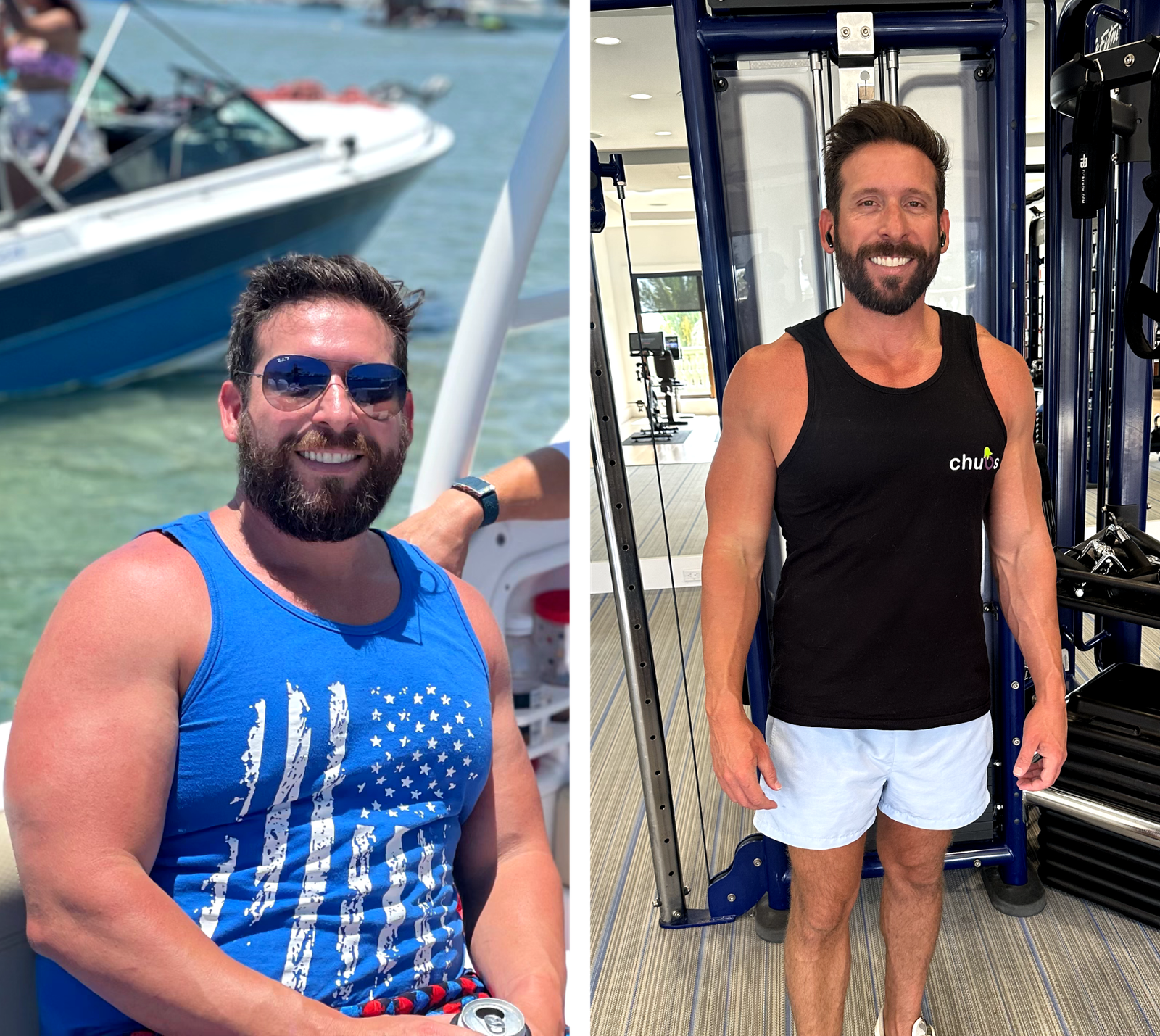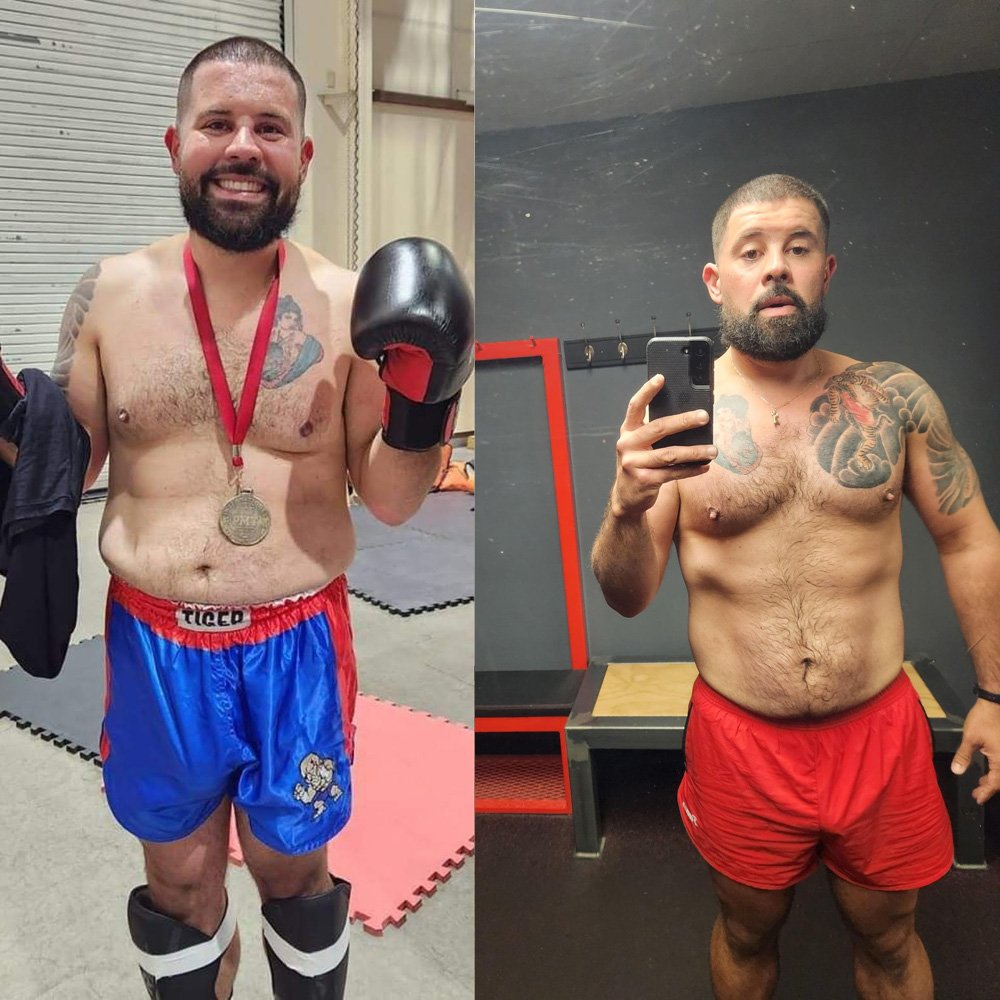
If you’re a man, you may have seen testosterone mentioned once or twice as you leafed through the pages of a health journal while waiting at the doctor’s office. The word may have even jogged a vague old memory from school when your sex education teacher gave the class that “talk” about the “differences between males and females.” Besides that, the lesson plan didn’t really discuss testosterone much further most of the time, and if they did, you probably didn’t pay much attention to it as you laughed and joked about the “birds and the bees” with your fellow classmates that day.
However, in this day and age, testosterone has become a serious topic in men’s health. And now that you’re grown up and have started to think about your future, you may have once again wondered, “what is testosterone? And why is it so important to me now that I’m older?”
In this article, we’ll go over testosterone and its role in the male anatomy, as well as what you can do to ensure that it remains maintained to preserve your health.
What Does Testosterone Do for Men?
As you may already know, testosterone is the male sex hormone primarily responsible for many physical and sexual characteristics in the male anatomy. During puberty, the testosterone hormone helps to develop various physical aspects in males, such as:
- Muscle growth and strength
- Sperm production
- Sex drive
- Deeper voice
- Facial hair growth
- Penis and testicle function

After puberty, testosterone continues to regulate and maintain these characteristics while managing metabolism, fat distribution, and mood as men age. However, once men reach their 30s, their testosterone levels begin to decline gradually at 1% yearly as they get older. Normally, this is a natural part of the aging process that is usually not a cause for concern. But when certain factors, such as genetics, trauma, or lifestyle, begin to affect the body adversely during this decline, it can lead to a further drop in your testosterone levels. When the body can no longer produce adequate amounts of testosterone to maintain the important aspects of your physical health, this condition is known as hypogonadism or low testosterone (Low T).
Once your testosterone is low, it can cause several debilitating symptoms such as:
- Low sex drive
- Weaker bone density
- Hair loss
- Constant fatigue
- Mood disorders
- Increased weight gain
- Decreased muscle mass and strength
Conversely, there are some instances that can cause an abnormal increase in testosterone for men. To alleviate the symptoms of hormone imbalances such as low T, physicians will typically recommend increasing your testosterone so that your testosterone levels can return to normal parameters. To achieve this, men may use a testosterone booster or testosterone supplements to increase their body’s testosterone production. However, without medical guidance, using these treatments can lead to abnormally high testosterone levels, or high testosterone (also known as hypergonadism), which can also cause unwanted physical complications such as:
- Excessive body hair
- Headaches
- High blood pressure
- Aggressive behavior
- Testicular shrinkage
- Acne
- Low sperm count
- Enlarged prostate
In many cases involving high or low testosterone, men are usually unaware of how the testosterone hormone is negatively affecting their physical and overall health. This is why many physicians recommend that men have their testosterone levels checked when they start experiencing unexplained physical symptoms.
Feeling Run-Down?
Take the Low-T Quiz Today
Our men’s clinic can restore your physiology, change your body composition and optimize your health to slow down aging and prevent health complications caused by low testosterone.
Take back your life and become a better you today!
Types of Testosterone
There are different types of testosterone that are present in the body. Typically, 98% of the body’s testosterone attaches itself to sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and albumin proteins, which inhibits the hormone’s function and prevents other tissues from using the attached testosterone. This is known as bound testosterone. The body then leaves the remaining 2% of the hormone unattached and available for use. This unbound testosterone is known as free testosterone and can act as a receptor for any cell in the body.
Total Testosterone
Total testosterone is a measure of the overall concentration of testosterone in the body that includes both the bound and unbound forms of the hormone. It is typically measured through a blood test, and is used to determine whether or not a person’s testosterone levels are within the normal range. This is usually tested to determine whether or not your testosterone levels are too high or too low. Abnormally low levels can indicate a condition such as hypogonadism, whereas excessively high levels may indicate that the body may be suffering from hypergonadism.
Free Testosterone
As previously discussed, free testosterone is the unbound, active form of the hormone that is available for use by the body’s tissues. It is also measured through a blood test and used to help diagnose the cause of abnormal testosterone levels. Unlike total testosterone, which measures both bound and unbound forms of the hormone, free testosterone provides a more specific measurement of the active form of the hormone. This measurement can help physicians better understand the patient’s testosterone levels and aid in making a diagnosis.
The Effects of Testosterone on the Body

The human body uses testosterone to regulate and maintain several biological functions in males. However, when the body is unable to maintain the hormone’s production for optimal testosterone function, it can also have an adverse effect on specific aspects of a man’s physical health, including:
The Reproductive System
Testosterone is primarily produced in the testes and also plays a crucial role in the production of sperm, and the function of the testicles and the penis. Typically, testicular interstitial cells, known as Leydig cells, will produce testosterone, which then stimulates sperm production in the seminiferous tubules of the testes. Thus, when your body suffers from testosterone imbalance, it can negatively affect your reproductive system’s normal processes and functions. Usually, low levels of testosterone can lead to decreased sperm production, whereas high testosterone levels can cause testicular shrinkage and also lead to a low sperm count. In both cases, low sperm counts due to abnormal testosterone levels may increase the risk of male infertility.
Libido
There are a few ways that testosterone can affect your libido. Low testosterone will typically cause your sex drive to decrease and, in some cases, may lead to erectile dysfunction. On the other hand, high testosterone can lead to an abnormally high sex drive. Although having an increased sex drive may not necessarily be a bad thing, an overly high sex drive can also lead to sexual disorders such as hypersexuality, which can also negatively affect your relationships and overall quality of life.
The Central Nervous System
Testosterone can also have a significant impact on the central nervous system. The hormone helps to regulate neurological functions in the brain and spinal cord, which can have an important role to play in cognitive function, memory retention, and gait. So when testosterone levels become unbalanced, it can lead to headaches, muscle weakness, and memory loss. In addition, testosterone plays a role in regulating the body’s stress response by modulating the activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which is responsible for the body’s response to stress. As such, abnormal testosterone levels can affect the body’s ability to cope with stress and may contribute to chemical changes in the brain that lead to alterations in mood, such as irritability, aggression, depression, and anxiety. And because of testosterone’s effect on the central nervous system, researchers have found that the hormone can even affect an individual’s sleep-wake cycle, as studies show that low testosterone levels can also lead to poor sleep quality and insomnia.
Hair Growth and Skin
Typically, when testosterone is produced, an enzyme known as 5-alpha reductase will convert some of your testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a form of the testosterone responsible for the development of your hair and skin.
Usually, DHT will bind itself to your hair follicles to stimulate hair growth. However, when your testosterone levels are unbalanced, DHT levels will also increase while residing inside the hair follicles, causing them to shrink and weaken. This is what usually causes the scalp to produce thinner hair, which may gradually fall out over a period of time. The DHT hormone will also make it more difficult for the scalp to produce more hair follicles and replace the weakened strands, which can eventually lead to more serious hair loss conditions such as male pattern baldness (MBP).
In terms of skin, testosterone also plays a primary role in producing collagen, which helps to maintain the skin’s elasticity and strength. The hormone also stimulates the sebaceous glands underneath the skin pores to produce sebum, a naturally secreted oil that helps to keep the skin hydrated to maintain its natural luster.
When your testosterone levels are high, it can lead to increased sebum production, which can cause the sebaceous glands to become inflamed and produce acne. In contrast, when testosterone levels are too low, it can lead to decreased collagen production and accelerate the signs of aging, such as wrinkles and dry skin.
The Circulatory System
Testosterone helps to dilate blood vessels and keep the blood flow flowing naturally throughout the circulatory system. So when your body is unable to maintain its testosterone function, it can lead to several cardiovascular and coronary complications, such as high blood pressure and atherosclerosis. Abnormal testosterone levels can also significantly raise your blood cell count and cause your blood to thicken, which can eventually lead to blood clotting and increase the risk of a stroke or heart failure.
The condition of your circulatory system can also affect a man’s ability to have erections. During an erection, the arteries expand to increase blood flow to the penis, which helps it enlarge and stiffen for an erection. When your testosterone levels are low, it can lead to poor blood circulation and make it more difficult for blood flow to reach the penis, leading to an increased risk for erectile dysfunction.
Weight
Testosterone helps to promote the breakdown of calories and fats into energy and evenly distributes it throughout the body. During this process, muscle cells will absorb some of this energy for growth while the body stores the rest in the fat tissue for later use. Typically, since muscle burns more calories than fat, the body usually continues to draw from the storage in the fat tissue to aid in muscle growth. However, if your testosterone levels are too low, your muscle mass decreases, making it more difficult to engage in physical activity and burn off calories stored in your fat tissue. Without a way to burn those calories, the accumulation of calories will cause your body fat to increase, eventually leading to weight gain and obesity.
How To Find Out What My Testosterone Level Is
It is absolutely imperative for men to check their testosterone levels once they begin experiencing certain unexplained symptoms. And the best way to find out your current testosterone level is through a testosterone test. Physicians will usually request total testosterone and free testosterone tests to help them to assess whether you have low or high testosterone and what may be causing the testosterone imbalance. These testosterone tests are usually measured in nanograms per deciliter (ng/dl) of blood, so your physician will usually require a blood sample for testing.
Typically, the normal testosterone level for a man will range between 300 and 1000 ng/dl. Naturally, if your testosterone levels are below 300 ng/dl, it will usually indicate a testosterone deficiency. Of course, if your testosterone levels are well above 1000 ng/dl, it is most likely a sign that your testosterone has gotten too high.
What Happens If I Have Low Testosterone Levels?
Low testosterone will typically cause men to exhibit symptoms such as muscle weakness, low sex drive, weight gain, weakened bone density, and joint pain. This can occur due to several factors, such as stress, certain dietary habits, poor sleep quality, and a lack of physical activity. Low testosterone can also occur if there are complications with important organs responsible for hormone production, such as the pituitary gland, hypothalamus, and testicles. If these low testosterone symptoms are allowed to persist, they can also lead to more serious medical issues such as erectile dysfunction, osteoporosis, diabetes, and obesity.
What Happens If I Have High Testosterone Levels?
High testosterone levels will also usually cause men to exhibit certain symptoms such as aggression, rash decision-making, excessive hair growth, low sperm count, and testicular shrinkage. High testosterone is usually caused by several factors, such as tumors on the adrenal gland or testicles or excessive testosterone supplementation. In some cases, high testosterone can lead to more serious medical complications such as high blood pressure and infertility in men.
Remedying Testosterone Imbalance
If you’re exhibiting signs of low testosterone, your physician may refer you to a Low T center to undergo testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). During TRT therapy, a hormone specialist can determine the cause of your low testosterone and administer testosterone injections to help provide the body with additional testosterone needed to replenish and maintain your testosterone levels so that they can once again reach normal standards. Depending on your case, the specialist may also recommend lifestyle changes, such as weight loss, regular exercise, and a healthy diet, to help you improve your overall health and further increase your testosterone levels in conjunction with the TRT treatment.
However, if you’re suffering from high testosterone, your physician will perform tests to see if your adrenal glands or testicles have damage or tumors that may be affecting your hormone production. If that is the case, they will likely refer you to a specialist that can remove the tumors and treat the damage to those organs before they address other ways to lower your testosterone. If your high testosterone is caused by external factors such as testosterone supplements or dietary habits, your physician may recommend that you stop using testosterone pills and reduce your intake of testosterone-boosting foods so that your testosterone levels can return to their normal parameters.
Whether you’re suffering from high or low testosterone, it is always important to consult with a physician or hormone specialist as you attempt to balance your hormone levels. They can provide experienced and knowledgeable recommendations and proper medical treatment to help you safely manage your hormone levels and alleviate your symptoms without further complications.
At the Renew Vitality Testosterone Clinic, we specialize in treating the symptoms of testosterone imbalance. Our experienced team of medical professionals can provide expert recommendations and effective treatment plans that can help you balance your hormone levels and improve your overall health. If you believe that you may be suffering from testosterone imbalance, contact Renew Vitality at 1-866-995-2371 and schedule an appointment at any of our hormone replacement clinics in the United States to learn more about our wellness plans and testosterone treatment options.
Resources:
- https://www.mja.com.au/journal/2013/199/8/global-trends-testosterone-prescribing-2000-2011-expanding-spectrum-prescription
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/press_releases/testosterone-and-memory
























